What is the market trend? Everything you need to know about how to research stock market trends
They say “the trend is your friend,” and this golden rule of trading applies to every asset in the market. Prices do not change randomly – their volatility is conditioned by many factors. When these factors coincide, certain trends are formed in the stock market. This guide will teach you how to discern these trends and perform market trend analysis to formulate a reliable trading strategy.
The article covers the following topics:
- What is meant by market trend? Definition and meaning
- Market trend analysis
- What you need to know about market trends
- How do you find and identify market trends?
- How do we know if the stock market trend is right?
- Know the market trends before you buy!
What is meant by market trend? Definition and meaning
Market trend means that the price action follows a certain trend over a certain period. Trends apply to all assets whose prices fluctuate, or when there is a change in trading volume.
A trend in the forex market and other financial markets is usually understood as a price movement that has formed over a certain period of time with a clear direction and strength. Trend is the main characteristic of price action – and traders use it to make trading decisions and increase their income.
According to the basics of technical analysis, price changes are always subject to specific rules.
These rules allow successful traders to predict the behavior of currencies and other market instruments. The systematic nature of changes in price charts makes it possible to trade in financial markets, predict the future behavior of assets and make the right trading decisions. Technical analysis includes countless indicators, advisors, and charting patterns that professional traders use as tools. Most of these tools are based on the concept of directional movement.
There are three main types of market trends:
- Bullish (uptrend) – when prices are rising. It is represented by a series of higher price peaks and higher lows. As long as each subsequent high is higher than the previous one, the uptrend remains.
- Bearish (downtrend) – when prices are falling. Any failed attempt to surpass the previous peak is an early indication of a trend reversal. A downtrend is characterized by a series of lower peaks and troughs.
- Sideways trend (flat market) – the absence of a clear movement in a certain direction (this condition is normal and more common in the market).
According to the Dow Theory, trends continue until there is an unmistakable sign of an end.
Trends can be categorized by duration, a trend can be:
- Long-term (main trend) lasting from six months to several years.
- Medium term (minor trend) is usually a correction within the main trend and can last from 1 to 6 months.
- Short term (minor trend) is a correction or consolidation that lasts less than 1 month. It could be a respite in an intermediate or major trend. Also, minor trends can be detected even on intraday charts.
Note: Do not confuse market trends with market sentiment. The latter means what traders believe about the upcoming price movement (their opinion does not necessarily represent real market conditions).
Directional properties
As a phenomenon in the financial market, the trend is characterized by three main characteristics:
1. Directional movement. This characteristic depends on the timeframe: the higher the timeframe, the less clear is the direction of the price movement. It is important to be able to distinguish between a price correction movement and a trend movement. In the case of the former, after some time, the price will return to its value and continue its movement within the trend channel.
2. Strength. The strength of the trend movement is determined by the slope of the price curve in the chart. Usually, price spikes or sharp moves in a trend are not very strong, as they are short-lived. A strong and influential trend movement is a stable update of the highs or lows (the slope of the price curve is about 45 degrees) and it lasts for a long time.
3. The time period. As expected, the more stable the trend movement is, the higher the time frame in which it clearly shows itself. The time period of a trend allows the trader to assess its strength and reliability.
Market trend analysis
To identify stock market trends, traders can use different approaches and techniques:
- Fundamental analysis. This means looking at the performance of the stock or the issuer of the stock in general. For example, a trader can notice an uptrend when 1) a company displays positive results in its financial statements more frequently; 2) the economic news shows that the industry continues to develop; 3) The global or domestic economy is on the rise as stock prices rise.
- Technical Analysis. In this case, various tools are used – they are called “trend indicators”. Moving averages (MA) are the most common and widely used. They reflect both the direction of price change and the strength of the trend.
- Volume analysis. With a developing trend, the price increase is accompanied by stable volumes or its rise is smooth. A significant drop in volumes or, conversely, an unexpected rise can be taken as a signal that the trend is over. When the stock price moves in another direction and the volume starts to grow, this means a possible trend reversal or correction.
Another approach worth mentioning is graphical market analysis, which can be seen as part of technical research. The most common visual tool is the trend line. Either the prices are above it, the trend is up, or below it, the trend is down, and they show the continuation of the trend.
Trend line
If the price continues to move in one direction for several weeks, the trader will notice that a resistance or support line is forming on the 4-hour daily chart. But if the trend has changed recently and a new movement has started to form, then at this point it is difficult to determine the boundaries of the trend line.
Trends without retracement are rare. Most of the time, after the price reaches the support or resistance line, it bounces off it. This pullback usually amounts to about 30% of the main move. With this in mind, trend lines can be drawn as follows:
- If the movement is up, a support line is drawn at the bottoms of the chart. Above it and parallel to it we can see the resistance line.
- When the movement is down, a resistance line is drawn at the highs, and a support line is drawn parallel to it.
- In the case of a flat market, the support line is drawn on the dips and the resistance line on the highs.
What you need to know about market trends
Trends are mainly shaped by four main factors:
- Governments.
- international transactions.
- assumptions/expectations.
- Supply and demand.
All of these areas are interrelated, as expected future conditions shape current decisions, which in turn create current trends. The government influences trends mainly through monetary and fiscal policies. These policies affect international transactions, which in turn affect trade and economic stability. Assumptions and expectations drive prices based on what the intrinsic value might be in the future. Ultimately, changes in supply and demand create trends as market participants compete for the best price.
Dow Theory also identifies some key characteristics of a trend that you should keep in mind:
- The trend will prefer to continue rather than end or reverse.
- The stronger the trend, the more likely it will continue.
- The trend can end at any time.
- If a trend has remained or continued under certain conditions in the past, this does not mean that it will form or continue under the influence of the same conditions.
How do you find and identify market trends?
Now that we know the theory, let’s move on to the practical part. You don’t need to have a huge trading experience to determine the direction of the stock market. Market analysis boils down to tracking the dynamics of price rises and falls. Here’s how that works.
The upside
An uptrend (uptrend) is price movement in an upward direction, in which each subsequent high is higher than the previous one, and each subsequent low is higher than the previous one.
This movement is clearly visible on currency charts: it is a curve that tends to reach new peaks in a certain period of time.
An upward trend refers to a gradual increase in price over a certain period. It is very important to perform the analysis only on a certain time period because the trend even on adjacent timeframes can be reversed.
Since the market can be strongly influenced by the actions of bulls (bulls) and bears (bears), traders must learn to identify whether this trend is natural or a result of overestimating the demand for a currency.
Downtrend
Downtrend (downtrend) is the movement of a stock to a price lower than the previous one. It will be there as long as there are lower tops and lower bottoms on the stock chart. A trader can save money if he decides to sell a falling stock. At the same time, other traders seek to take advantage of the downtrend by buying and selling short. The downtrend can be identified using trend lines and moving average lines.
lateral direction
A sideways trend is also referred to as a flat trend, which means that for a trend to be neutral, the price of an instrument moves up and down in a particular price range.
In other words, a sideways, or flat, trend in Forex appears on a price chart as highs and lows that occur sequentially at approximately the same level.
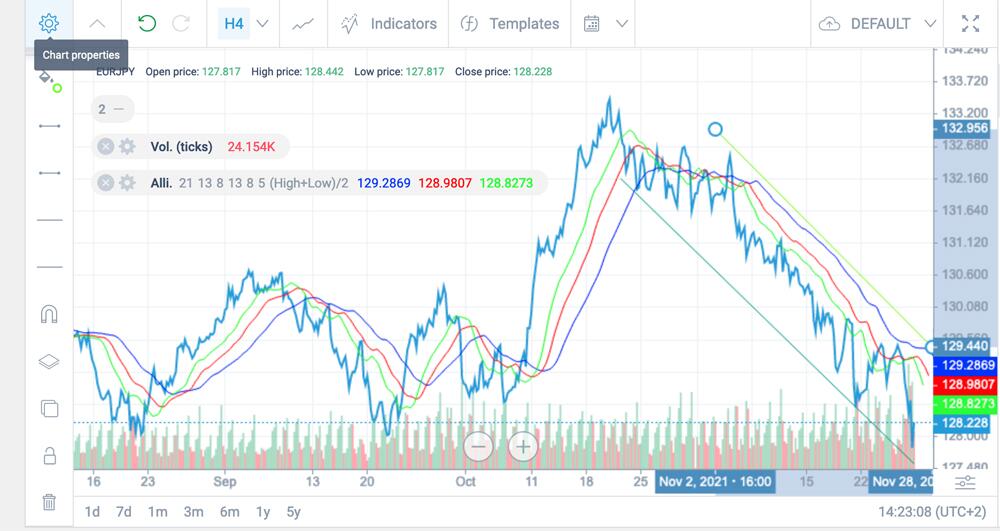
You can see an example of a sideways trend in the following EURUSD chart:
lateral directions
As mentioned earlier, sideways trends are at the time of correction. This means that the price of an asset can go in any direction, even if it is unexpected. How do you detect a sideways trend? This usually happens when you see the stock price making sudden highs and turns without any clear up or down trend. Such a situation can go on for several weeks or even months leaving traders confused (also causing market participants to buy or sell in a chaotic manner).
Sideways trends are often triggered by some political or economic action and news. History shows that:
- Highs in a bull market are strong, while bounces are weak.
- Highs in a bear market are weak, while bounces can be strong.
- Each market (bear or bull) will have at least three sideways trend cycles, each lasting 2 to 8 weeks.
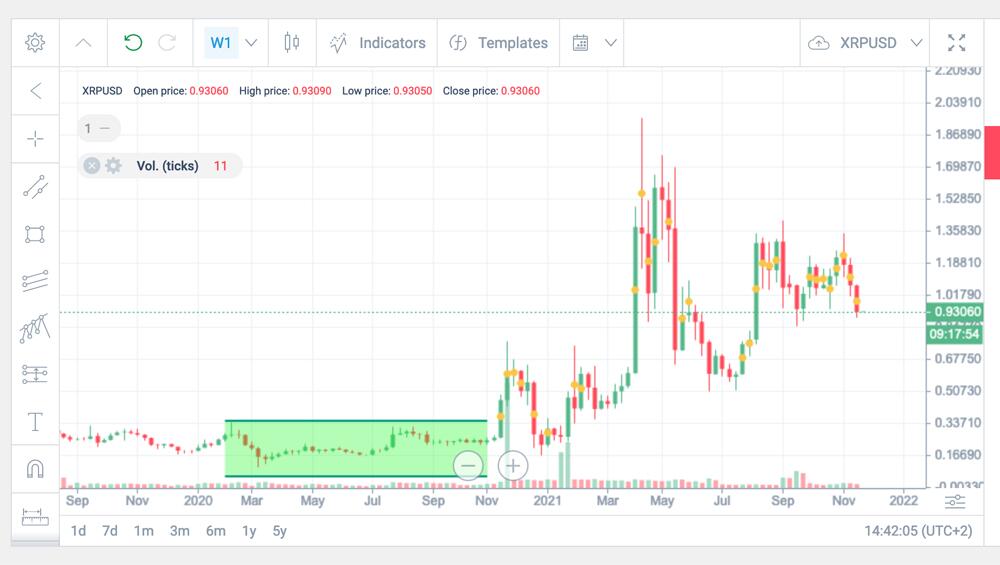
Long term trends
According to analysts, the long-term price trend lasts from six months to five years. It is also called the “major” or “primary” direction. Note that it is formed by medium term trends which can be in opposite directions.
For charting and technical analysis of long-term trends, traders use the weekly and monthly timeframes. Long-term trends are of interest to large market participants and investors who prefer to hold assets for several years (in the stock market, for example).
But even if you are trading in the medium term, knowing the current long-term trend can help you compare data obtained from different timeframes. Besides, it is used when you work with multiple analytical tools and need to align information and make decisions in shorter periods. Important events and the global economy can affect the price of assets at any moment, but the long-term trend usually prevails despite what is happening in the market.
To identify a long-term trend, traders usually combine the Stochastic Oscillator with the ROC (Rate of Change) indicator. The latter is calculated by the following formula:
ROC = (Pt / Pt-n) x 100%
where:
Pt – price of the current position;
Pt-n – the price of a similar position from some time ago
When analyzing long-term trends, traders usually apply the ROC indicator to the 26- or 52-week timeframes, as shown in the chart above.
How do we know if the stock market trend is correct?
To make more accurate forecasts, you need to be able to use reliable market research tools and methods. Here are the tools that traders often use to test their theories.
trend line
A trend line is drawn on a price chart by connecting at least two extreme points following each other in a one-way (up or down) movement. By drawing a parallel straight line, you form a channel in which the price will move.
How do you determine direction using this tool? The price of the asset will move somewhere between these lines. Thus, when prices go up, you should buy (expecting the price to increase), and when prices move down – you are short (expecting that the current stock price will go down).
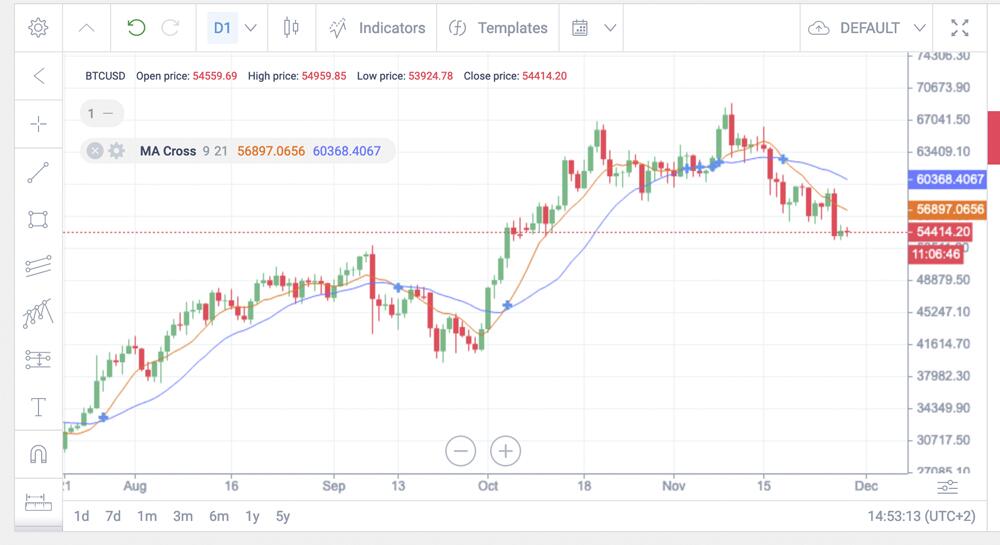
Moving average
A moving average is often used with a trend line to get a more objective and fair view. The price always moves near its average value but it can deviate in one direction or the other.
If yesterday’s closing price is above the moving average level (see chart), an uptrend is coming. If yesterday’s closing price is below the same moving average, the value of the asset is likely to decline.
The orange middle line is used as a confirmation signal. If the price closes above the weekly average, the market will continue to go up for a long time after that, in the opposite case – the market will have a downtrend. Despite its reliability, the moving average indicator can be lagging, which makes it less suitable for short-term trading.
horizontal size
By analyzing horizontal volume, a trader can identify a value area and understand where the price is in relation to a particular level. The volume is interpreted in the following way: if the price level is above this area, then you should buy in the medium term, if the price is below that area – then you should sell the asset.
You can stick to this trend as long as the price area does not move, i.e. no volume will accumulate and exceed the size of the previous value area. When enough volume is accumulated, the stock gains momentum, and the trend continues or reverses.
Know the market trends before you buy!
To trade the stock market successfully, you need to be aware of price trends: they reflect the mood of traders and show you the right time to enter or exit. Try to project a broader picture: you should pay attention to both news and asset performance. Using technical indicators along with market research is what makes the best trading strategies.
Frequently asked questions about the trend in the forex market
What is meant by the direction of the stock market?
It is the direction (upward or downward) in which the price of an asset moves during a certain period. Trends provide general information about the potential price movement of a stock.
How do you find market trends?
This is done by analyzing the economic background and performing technical analysis. Open the chart by the corresponding arrow symbol, look at the price movements and look for patterns that allow you to predict price fluctuations.
How do you know if the stock market is going up or down?
The most used tool is the trend line because it allows detecting the channels in which the price is moving. If there is no clear movement in either direction, traders will experience a flat market (it is a period of volume accumulation).
How do you find stocks with an uptrend?
There are several signs of an uptrend: 1) the closing and opening prices of assets are rising day by day (or week by week if we follow long-term strategies); 2) the price of the asset remains above the moving average; 3) The rate of change (RoC) indicator crosses the zero line.
What are the three types of trend analysis?
Fundamental analysis – a review of the stock’s performance and its economic background in general. Technical analysis – application of technical indicators to the price chart of an asset. Volume Analysis – Track volume increases, decreases and backlogs.